RFI
Joint Lab with Rete Ferroviaria Italiana - RFI

The ARCES-RFI Joint Lab was established in 2018 as a mean for continuous management and monitoring of intensive joined research.
Common to this joint lab are the context (critical systems design), the target Safety Integrity Level (SIL4) and the target TRL (TRL5). Specific lab aspects are multi-disciplinarity and technology convergence. Main disciplines involved are electromagnetic fields, antennas, structural dynamics, sensor fusion, signal processing, machine learning and digital design, while the addressed enabling technologies are wireless power transfer, heterogeneous architectures on SOCs, MEMS sensors, GaN based power amplifiers, and ultra-low power smart and wireless embedded platforms. Current research in the ARCES-RFI joint lab moves along three orthogonal research vectors: on-board train positioning equipment, ground side rail occupancy equipment, and structural health monitoring of the overhead line (catenary).
On board train positioning
On-board train positioning methods are investigated at the ARCES-RFI Joint Lab. The approach taken complies with the ERTMS/ETCS (European Railway Traffic Management System/European Train Control System) specification and it is based on the dead-reckoning principle. The expected outcome is a prototype consisting of the combination of an odometer and an intermittent position synchronization module named BTM (Balise Transmission Module). The BTM is an energy feeder-data receiver module that powers up passive beacons located along the rails (Eurobalises) and captures position dependent telegrams reflected by the beacons. The architecture is redundant and it is implemented in an extremely small form factor thanks to the extensive use of SOC technologies and innovative system integration solutions.
Rail track occupancy detection
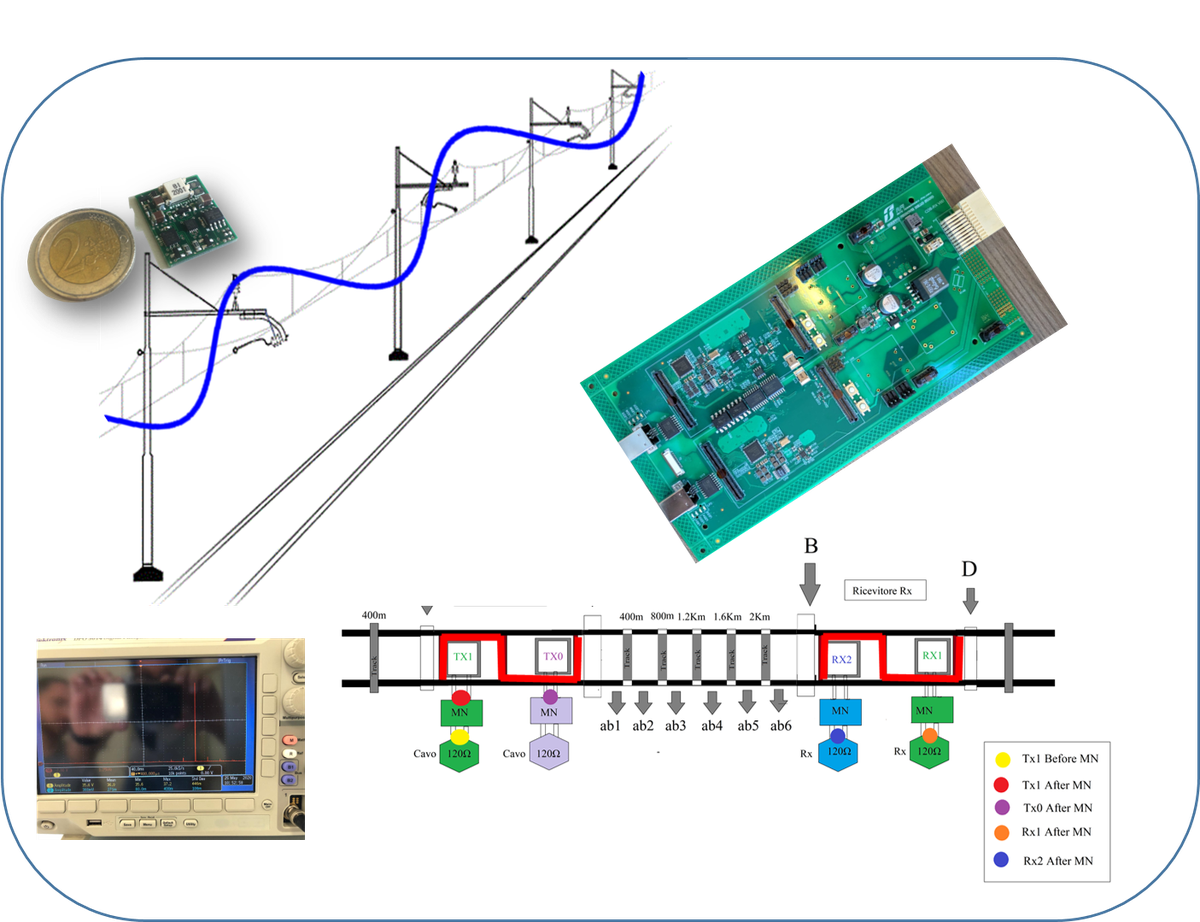
A new design of the traditional track circuit for the detection of the presence of a train on rail track segments is investigated at the ARCES-RFI Joint Lab. The approach taken is audiofrequency based and requires intensive modeling and signal processing activity. The rail track is modelled as an ordinary trasmission line. As shown in the figure Tx and Rx are connected to loops inductively coupled to the rail track throough s-shaped joints. The purpose of this research is to develop a prototype of the entire Tx - track - Rx chain and to validate the outcome in the RFI large test circuit located in Bologna (Circuito S. Donato, with over 5.5 Km tracks) in late 2020-early 2021. This is an interdisciplinary and multipartner project where the outcome of ARCES based electromagnetic design and signal processing are deployed in hardware solutions implemented by ARCES and other Universities under the direction of RFI.
Health monitoring of the overhead line
The third and most recent line of joined research carried out at the ARCES-RFI Joint Lab is in the domain of infrastructure health monitoring and concerns the Implementation and deployment of predictive algorithms of the catenary wear and tear.Here the goal is to design a ground side smart and sustainable sensor based system-of-systems for continuous monitoring of the risk influencing factors of the pantograph-catenary interaction, in order to trigger predictive maintenance, detect anomalies and identify faults origins. This research is managed by RFI, ARCES and CINI, the Italian National Interuniversity Consortium for Informatics.
RETE FERROVIARIA ITALIANA
-
RFI official website
RFI, with more than 25.000 employees, is the largest infrastructure management company in Italy, and one of the largest in Europe. RFI is responsible for the infrastructure of the Italian railway system (more than 16.500 Km), manages the investments for the upgrading of the railways, develops the relevant technology and promotes the integration of the European Railway Network.
location
ARCES-RFI JOINT LAB